Notes
Types of locks -
- Write lock
- Read lock
- Predicate lock - Lock where multiple rows are locked for reads(WHERE clause) All of these locks are long locks(Meaning all are acquired first and then all are released)(2 Phase locking)
If we wanna improve performance(and decrease isolation levels), we can reduce long locks to short locks.
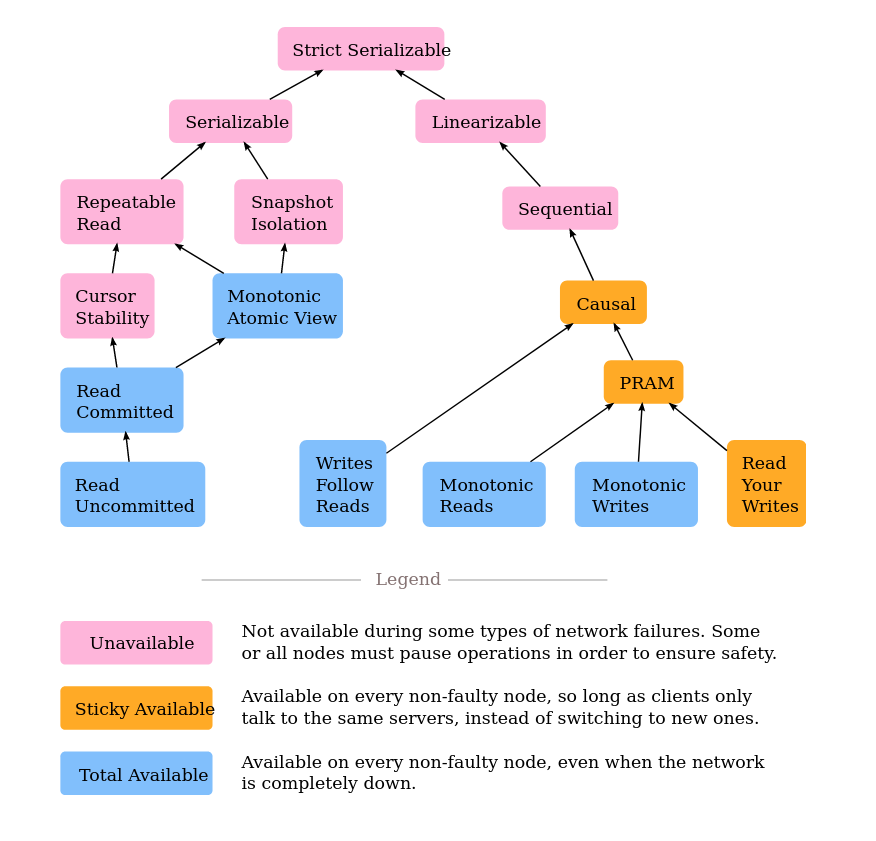
Types of anomalies -
Phantom Reads is we do a search condition (using WHERE clause) and then Read1, Write1 and Read2. Read1 =/= Read2. Fuzzy Reads is Read1, Write1 and Read2. Read1 =/= Read2. Dirty Reads is where we can read an uncommitted value of a transaction. Read Skew is where Tx 1 has a write(x) and then read(y) and Tx 2 has a write(y) and then read(x) causing the system to be non-serializable. Write Skew is where Tx 1 has a read(x) and then write(y) and Tx 2 has a read(y) and then write(x) causing the system to be non-serializable.
| Isolation Level(In decreasing order of levels) | Write lock | Read lock | Predicate Lock | Phantom Read | Fuzzy Reads | Dirty Read |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serializability | Long Lock | Long Lock | Long Lock | No | No | No |
| Repeatable Read | Long Lock | Long Lock | Short Lock | Yes | No | No |
| READ COMMITTED | Long Lock | Short Lock | Short Lock | Yes | Yes | No |
| READ UNCOMMITTED | Long Lock | No Lock | No Lock | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Just the exclusion of these 3 anomalies doesn’t mean that serializability is achieved.
We need to define read skew and write skew and